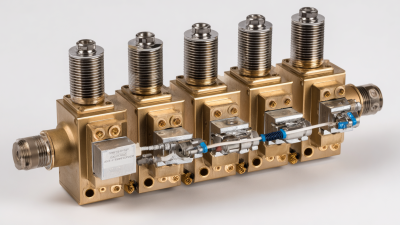
Unlocking the Power of Air Solenoids: A Comprehensive Guide for Engineers and Developers
In today's rapidly advancing technological landscape, the demand for efficient automation solutions has surged, particularly in industries such as manufacturing, automotive, and robotics. Air solenoids, critical components in pneumatic systems, play a pivotal role in controlling fluid dynamics with precision and reliability. According to a recent report by Fortune Business Insights, the global solenoid valve market is expected to reach $4.8 billion by 2026, driven largely by the increasing need for automated systems. Engineers and developers must harness the full potential of air solenoids to enhance operational efficiency and product performance. This comprehensive guide aims to provide an in-depth understanding of air solenoids, exploring their mechanisms, applications, and best practices for implementation, ensuring that professionals are well-equipped to leverage these vital components in their projects.

Understanding Air Solenoid Basics: Key Concepts for Engineers
Air solenoids are essential components in various engineering applications, and understanding their fundamentals is crucial for professionals in the field. These devices convert electrical energy into mechanical motion, enabling precise control in pneumatic systems. They operate by creating a magnetic field that moves a plunger, which can either open or close a valve. Engineers must grasp key concepts such as solenoid response time, force output, and the relationship between voltage and current to effectively integrate air solenoids into their designs.
Recent innovations demonstrate the versatility of pneumatic technology, as seen in projects that utilize gas thrusters for drone control and pneumatic systems for robotic movements. Such advancements highlight the potential of air solenoids beyond traditional applications, showcasing their role in enhancing functionality and performance. By leveraging the basic principles of air solenoids, engineers can explore new avenues in automation and robotics, paving the way for cutting-edge solutions.
Unlocking the Power of Air Solenoids: A Comprehensive Guide for Engineers and Developers
| Feature | Description | Applications | Specifications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Actuation Type | Electromechanical device that converts electrical energy into linear motion. | Automation systems, industrial machinery, automation robots. | Voltage: 12V - 24V; Power: < 10W. |
| Response Time | Rapid response time, typically in milliseconds. | Used in applications requiring quick on/off control. | Less than 20 ms. |
| Control Modes | Can be controlled electronically via relays or PLCs. | Used in conveyor systems, packaging machines. | Can handle PWM signals for improved control. |
| Size and Mounting | Compact design allowing for versatile mounting options. | Fit in tight spaces in machinery. | Dimensions: Varies by model, typical range 50mm x 50mm. |
| Durability | Designed for high-cycle applications with longevity in mind. | Suitable for repetitive tasks in manufacturing. | Lifecycle: Up to 1 million cycles. |
Benefits of Air Solenoids in Automation and Control Applications
 Air solenoids have emerged as essential components in automation and control applications, providing reliability and efficiency in various industries. According to a recent report by MarketsandMarkets, the global market for solenoid valves, which includes air solenoids, is projected to reach $5.48 billion by 2025, growing at a CAGR of 5.8%. This growth underscores their critical role in systems requiring precise control of airflow and pressure. With their ability to operate at high speeds and with minimal energy consumption, air solenoids are ideal for applications ranging from fluid control to automated machinery.
Air solenoids have emerged as essential components in automation and control applications, providing reliability and efficiency in various industries. According to a recent report by MarketsandMarkets, the global market for solenoid valves, which includes air solenoids, is projected to reach $5.48 billion by 2025, growing at a CAGR of 5.8%. This growth underscores their critical role in systems requiring precise control of airflow and pressure. With their ability to operate at high speeds and with minimal energy consumption, air solenoids are ideal for applications ranging from fluid control to automated machinery.
Implementing air solenoids can lead to significant enhancements in automation processes. Their quick actuation times and low maintenance needs result in improved operational efficiency and reduced downtime. For instance, research from the International Journal of Automation and Control indicates that systems utilizing air solenoid technology can achieve up to a 30% increase in overall productivity. This efficiency is critical for industries like manufacturing, where every second counts.
Tips: When integrating air solenoids, it’s advisable to pay close attention to the voltage ratings and environmental conditions to ensure optimal performance. Additionally, regular maintenance checks can extend the lifespan of these components significantly. Lastly, utilizing solenoids with fail-safe designs can enhance system reliability, especially in mission-critical applications.
Selecting the Right Air Solenoid: Factors to Consider
When selecting the right air solenoid, engineers and developers must evaluate several key factors to ensure optimal performance in their applications. The first consideration is the solenoid's operating pressure range, which needs to match the working environment of the project. A solenoid with inappropriate pressure specifications can lead to operational failures or inefficiencies, making it crucial to analyze the intended use case thoroughly. Additionally, the size and form factor of the solenoid play significant roles, especially in compact designs where space is limited. Choosing a solenoid that aligns with the project's mechanical constraints is essential for successful integration.
Another important aspect is the solenoid's response time and duty cycle. For applications requiring quick actuation, such as automated pick-and-place systems, a solenoid with rapid activation and a suitable duty cycle will enhance overall responsiveness and productivity. This is particularly relevant in prototyping scenarios where efficient control systems are necessary to refine robotic operations. Ultimately, understanding these factors helps in selecting the most appropriate air solenoid, enabling engineers to design sophisticated systems that meet specific operational goals.
Air Solenoid Selection Factors
Common Challenges in Air Solenoid Implementation and Solutions
When implementing air solenoids in engineering projects, many developers face common challenges that can hinder performance and efficiency. One major issue is leakage in the system, which can lead to inaccurate operation and increased costs. To mitigate this, it is crucial to ensure that all connections are secure and properly sealed. Regular maintenance checks can also help identify and rectify any leaks early on.
Another challenge is achieving the desired actuation speed and force. Variability in air pressure or the solenoid’s design can affect its responsiveness. Engineers should consider using adjustable pressure regulators to fine-tune the system's performance. Additionally, selecting the right size and type of air solenoid for the application can significantly enhance reliability and efficiency.
Tips: Always consult the manufacturer’s specifications for installation and adjustment to avoid premature failure. Additionally, incorporating fail-safes in your design can help manage unexpected situations, ensuring that the solenoid operates within its intended parameters. Testing the system under different conditions can also provide valuable insights and drive improvements in the overall implementation process.
Maintenance Tips for Enhancing Longevity of Air Solenoids
 Air solenoids play a crucial role in various pneumatic systems, making their maintenance essential for optimal performance. Regular maintenance not only increases the longevity of these components but also enhances system efficiency. According to industry reports, poorly maintained solenoids can lead to a 20-30% drop in system efficiency due to contaminants that affect valve operation. To prevent this, it’s vital to keep the solenoids clean and free from dust or debris, which can cause operational failures.
Air solenoids play a crucial role in various pneumatic systems, making their maintenance essential for optimal performance. Regular maintenance not only increases the longevity of these components but also enhances system efficiency. According to industry reports, poorly maintained solenoids can lead to a 20-30% drop in system efficiency due to contaminants that affect valve operation. To prevent this, it’s vital to keep the solenoids clean and free from dust or debris, which can cause operational failures.
Incorporating advanced monitoring solutions can significantly mitigate maintenance issues. For example, using diagnostics that monitor solenoid performance and diagnose potential failures early can extend their service life. Research indicates that implementing predictive maintenance strategies can reduce downtimes by up to 50%, leading to substantial cost savings. Engineers and developers should also adhere to manufacturer guidelines for cleaning and inspecting their solenoids regularly, along with checking for signs of wear or corrosion, which are common causes of failure. These proactive measures can contribute to a robust and reliable system.
Get in Touch
570 Alden Road Unit #10, Markham Ontario Canada, L3R 8N5
Quick Links
Featured Products
Industries